No products in the cart.
Return To ShopUnderstanding Asthma – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overview
Asthma is a chronic condition that inflames the airways that carry air to the lungs. Inflamed airways are very sensitive and react to things in the environment called triggers, such as substances that are inhaled.
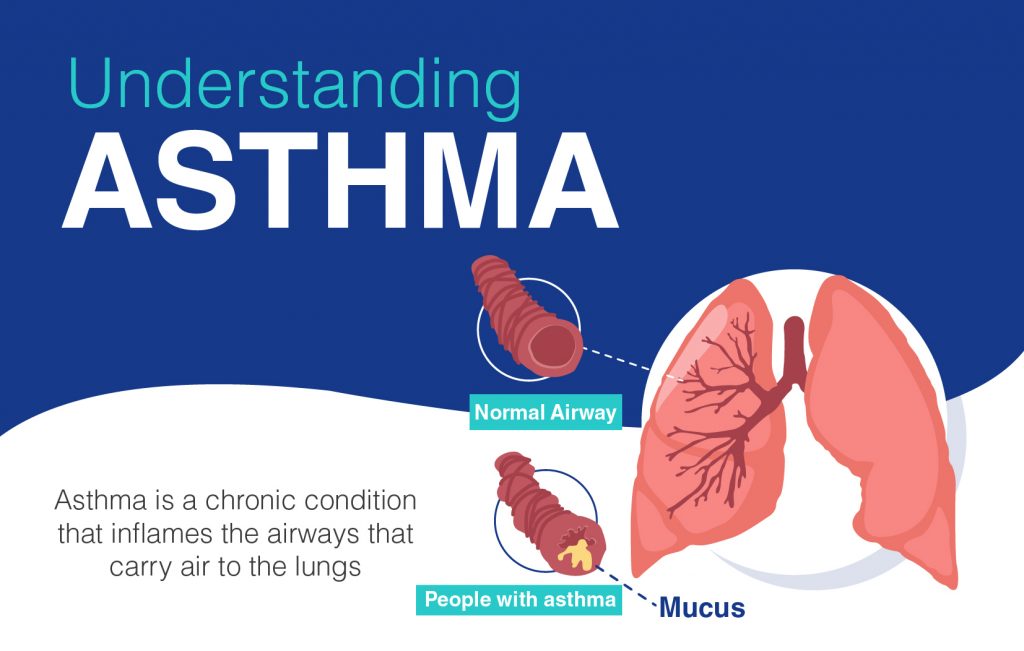
When the airways react, they swell and narrow even more, and also produce extra mucus, all of which make it harder for air to flow to the lungs. The muscles around the airways also tighten, which further restricts airflow.
Asthma can be life-threatening if proper treatment is delayed.
What are the symptoms of Asthma?
Symptoms of Asthma can include:
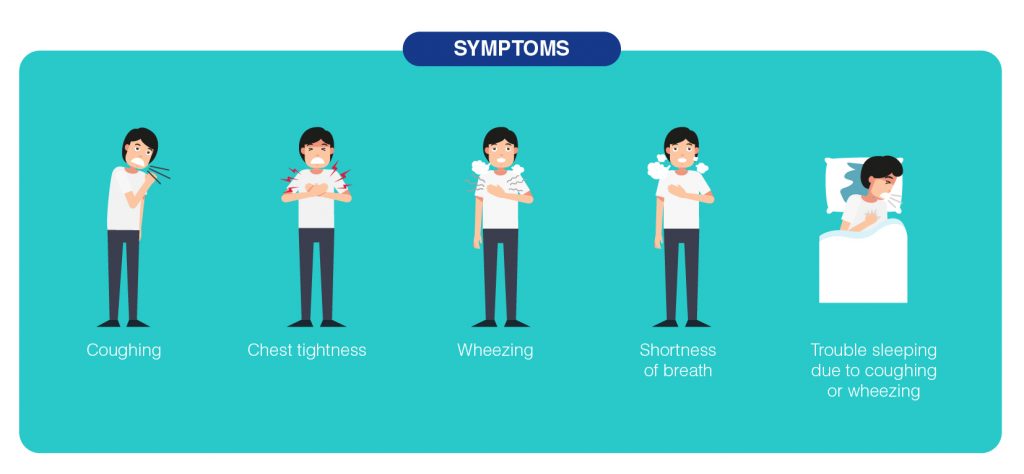
- Coughing
- Chest tightness
- Wheezing, a whistling sound when breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Trouble sleeping due to coughing or wheezing
What is an Asthma attack?
An asthma attack is a sudden worsening of symptoms. With an asthma attack, the airways tighten, swell up, or fill with mucus.
What causes Asthma?
The underlying cause of asthma is not known, but it’s probably due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
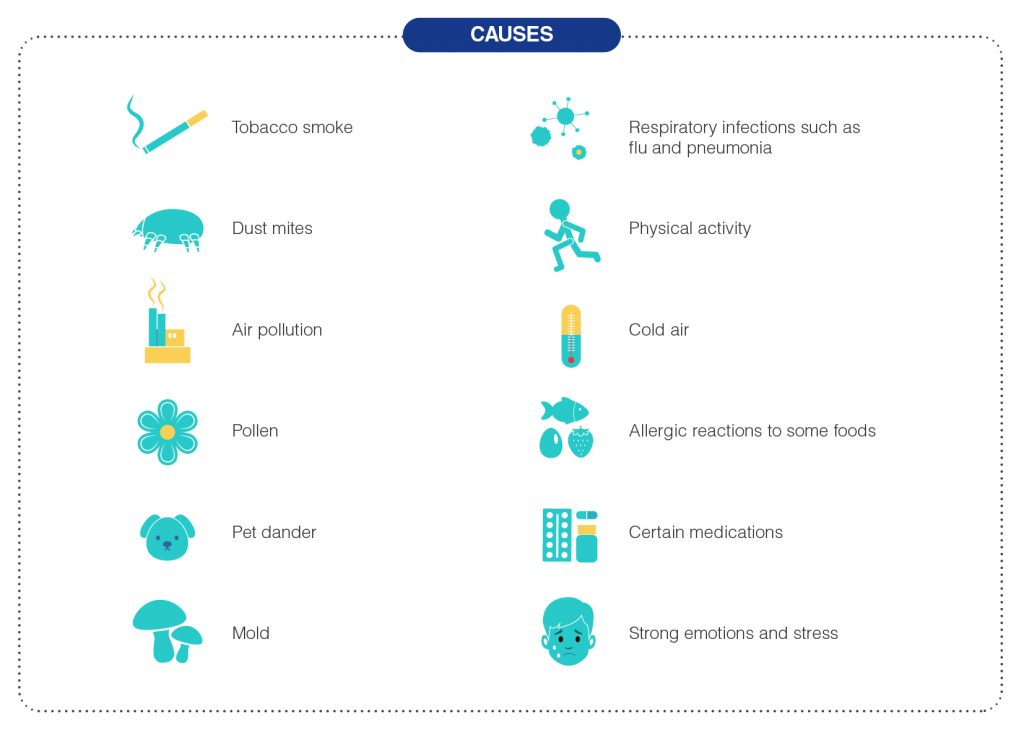
Symptoms of asthma can be caused by triggers. Common asthma triggers include:
- Tobacco smoke
- Dust mites
- Air pollution
- Pollen
- Pet dander
- Mold
- Respiratory infections such as flu and pneumonia
- Physical activity
- Cold air
- Allergic reactions to some foods
- Certain medications
- Strong emotions and stress
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition in which stomach acids back up into the throat
How is Asthma classified?
Asthma is classified into four general categories:
- Mild intermittent: Mild symptoms up to two days a week and up to two nights a month
- Mild persistent: Symptoms more than twice a week, but no more than once in a single day
- Moderate persistent: Symptoms once a day and more than one night a week
- Severe persistent: Symptoms throughout the day on most days and frequently at night

What are the types of Asthma?
There are following types of Asthma:
- Adult-onset asthma: Asthma can develop at any age, and adult-onset asthma is a description used for adults who develop asthma.
- Exercise-induced Asthma: This form of asthma is triggered by physical activity.
- Allergic asthma:
Patients with asthma allergy are asked to avoid certain food items as they may worsen their symptoms. Food allergies and asthma together can be challenging for you. The basic definition of a food allergy encapsulates the over-reaction of the body’s immune system to certain harmless proteins by releasing a chemical called histamine. If someone has developed a food allergy, symptoms like hives, rash, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may be observed. The food items like eggs, Milk, Peanuts, Tree Nuts (Cashews, Almonds, Filberts, Etc.), Soy, Wheat, Fish, Shellfish, And Shrimp are usually associated with food allergies. Avoiding these food items can prevent food allergies and asthma attacks.
Asthmatic patients should avoid foods with omega-6 fatty acids and trans-fats in them as they trigger asthma symptoms and worsen the condition. Processed foods and some margarine must also be avoided.
- .
- Nonallergic asthma: It is caused by irritants in the air not related to allergies such as burning wood, cigarette smoke, cold air, air fresheners, perfumes.
- Occupational asthma: It is caused by triggers in the workplace such as dust, dyes, gases and fumes, industrial chemicals, animal proteins, and rubber latex.
- Nocturnal asthma: It is one of the asthma types in which it becomes difficult for people suffering from asthma to cope at night, and they experience symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath which, in turn, affect their sleep. People with uncontrolled asthma usually experience these symptoms. If experts believe the circadian rhythm is the main culprit here. Additionally, nocturnal asthma can also be triggered by too much humidity, a dirty pillowcase, a big meal before sleep, undiagnosed sleep apnea etc..
- Asthma-COPD overlap: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a collection of lung diseases that cause breathing problems and obstruct airflow. Most people with asth-ma will not develop COPD, and many people with COPD don’t have asth-ma. Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome occurs when a person has these two diseases at once.
- Medication asthma: In this type of Asth-ma, symptoms are triggered by medications.
- Cough-variant asthma: This type of asth-ma is characterized by a persistent, dry cough
Exercises For Asthma Patients
There is a wrong notion that physical activities can aggravate asth-ma allergy. But the matter of fact is that some exercises are really helpful for asth-ma patients. Exercises like swimming help in building up the muscles used for breathing. Also, it increases lung function and cardiopulmonary fitness. Yoga is another amazing exercise for people who have asth-ma. Additionally, asth-ma patients can try other physical exercises like walking, biking, hiking, golf, gymnastics etc., to maintain their fitness regime. However, sports like cross-country skiing, ice hockey, and endurance sports like soccer and long-distance running may trigger asth-ma and hence, must be avoided.
Tips For Exercising With Asthma
- Before starting with your daily fitness regime, do some warm-up exercises.
- Wear a scarf or a mask over the nose and the mouth to keep yourself protected in the cold weather.
- If you also have some allergies, especially pollen allergies, it is better to stay indoors when pollen counts are high.
- Do not exercise outdoors if the level of pollution is high.
- Avoid exercising when sick.
- Do not overexert yourself while exercising.
- In case of emergencies, it is advisable to carry an albuterol inhaler.
What are the risk factors for Asthma?
A number of factors increase the chances of developing asth-ma. These include:
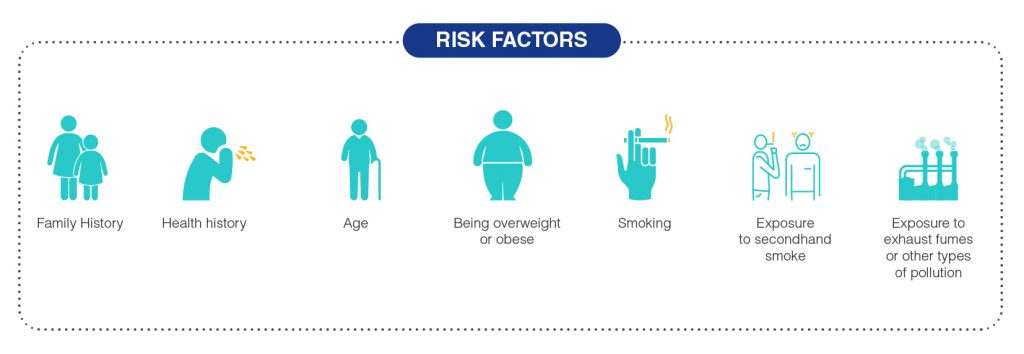
- Family History: Children born to parents with the disease are more likely to develop it.
- Health history: People diagnosed with certain conditions, including allergies and eczema, are more likely to be diagnosed with asth-ma.
- Age: Asthma can develop in adulthood, but the majority of asth-ma diagnoses are made during childhood.
- Exposure to occupational triggers, such as chemicals used in farming and manufacturing
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to exhaust fumes or other types of pollution
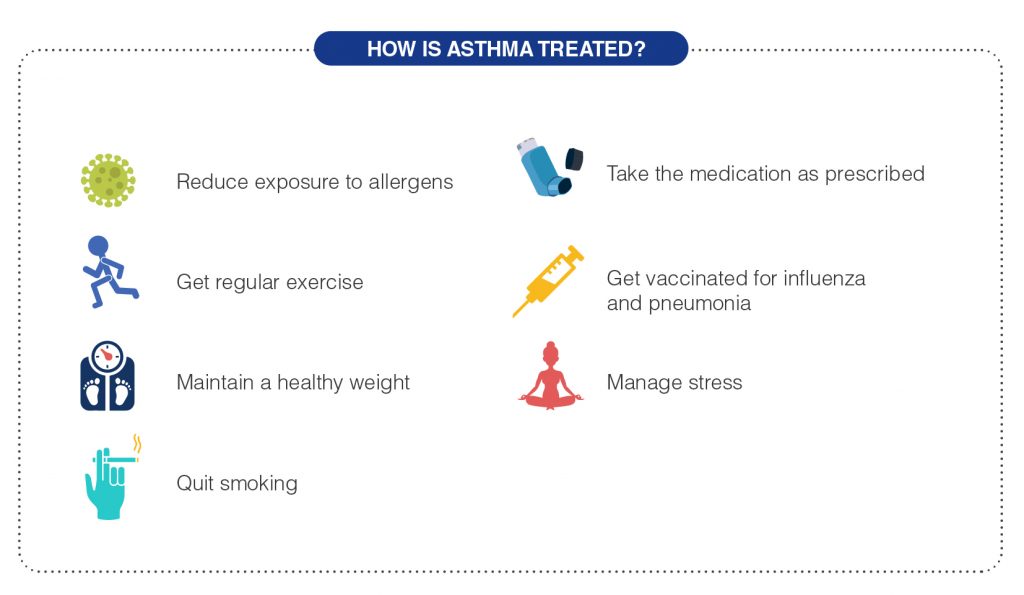
How is Asthma treated?
Asthma can’t be cured, but its symptoms can be controlled.
Managing asth-ma usually involves below:
- Identify and avoid asth-ma triggers
- Reduce exposure to allergens that can trigger an asth-ma attack
- Get regular exercise. Regular exercise can strengthen the heart and lungs, which helps relieve asth-ma symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight can worsen asth-ma symptoms, and increases the risk of other health problems.
- Quit smoking.
- Take the medication as prescribed.
- Get vaccinated for influenza and pneumonia
- Manage stress as stress can be a trigger for asth-ma symptoms.
Are You Controlling Your Asthma, Or Is It Controlling You?
Patients with asthma should be able to enjoy their busy lives without constant, debilitating symptoms. If you or your child has chronic asth-ma, make sure you are in control of your asth-ma. Learn about the risk factors, symptoms, and best practices for controlling your asth-ma.
Identify And Avoid Asthma Triggers
Asthma doesn’t “flare-up.” Coughing and wheezing usually signal that you’ve been triggered by something.
Knowing what asthmatic triggers you and what environmental factors make it harder for you to breathe will help you avoid certain triggers and maintain your asth-ma maintenance. Recognizing how to avoid triggers can keep your asth-ma from getting worse.
If you are coughing or experiencing shortness of breath without other respiratory symptoms, take note of what’s around you. You will soon learn to identify the real triggers behind your symptoms.
10 Common Asthma Triggers (1)
- Smoke
- Perfumes and Scents
- Cold and Dry Air
- Rain and Adverse Weather Conditions
- Activity and Exercise
- Pet Dander
- Pollen
- Dust Mites
- Food Allergies
- Respiratory Illness
Over time, you’ll be able to identify patterns and triggers. Log the information in your asth-ma journal or asth-ma action plan. Your medical professional will want to know which triggers you’ve identified. By working with your doctor, you help them to know which asth-ma medications can give you better long-term control of your asth-ma.
Stay Active to Control Asthma
Practice deep abdominal breathing when you start to feel yourself getting anxious or anxious to prevent asth-ma from dominating your life. In turn, this will ease the tension of the muscles in your throat, which will reduce the process of narrowing your airway. Finally, maintain a healthy sleep schedule to help avoid asth-ma triggers. By controlling asth-ma, you’ll be able to have a healthy, active lifestyle.
Is It More Than Asthma?
While this seems counterintuitive, regular exercise can help control your asth-ma. Strengthening your lungs will help give you more control over your asth-ma. One study showed that 30 minutes of daily exercise meant participants were 2.5 times more likely to have control of their asth-ma.
Walking is a great choice for all fitness levels. This form of exercise is gentle on the body, which makes it easier to breathe. Walk outside on warm days. Dry cool air can trigger asth-ma. During winter, you can walk on a treadmill or indoor track.
A common mistake that people who live with asth-ma make is assuming that all lung issues are related to their asth-ma. It’s possible that your cough is a symptom of a respiratory illness or other condition.
- Colds & Flu
- COVID-19
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Sleep Apnea
- Sinus Infections
- Acid Reflux
Automatically assuming that all breathing issues are asth-ma-related can result in worsening conditions that could damage your lungs. It can also increase your use of asth-ma medicine or quick-relief inhalers unnecessarily. For out-of-the-ordinary or long-lasting symptoms, consult your healthcare professional immediately.
Clean the House
Many people suffering from asth-ma know the importance of controlling their disease to stay healthy. But often, the disease works against us and we don’t realize how much we’ve been suffering from what we assume is only the aftermath of the disease. If you suffer from asth-ma, do this: identify and avoid your triggers and stay active to control your asth-ma
The most common household triggers include mold, dust, and pets. Pets are great companions but they can trigger asth-ma symptoms. Make sure you take regular times throughout the week to dust and vacuum your home. This will help reduce your exposure to pet dander and other pet-related allergens.
Consider The Weather
The weather has an effect on those with asth-ma and can cause breathing issues. Be aware of the weather before leaving your home and prepare accordingly.
For instance, air quality during fire season or extremely humid weather can trigger asth-ma. So if the weather outside is less than ideal, people with asth-ma should grab a scarf or something to cover your face. During allergy season, keep track of pollen levels and avoid going outside when they’re really bad.
Spirometry Helps with Controlling Your Asthma
In this article, we talked about asth-ma triggers, how to identify them and avoid them, and why being active is critical to controlling the condition. We then talked about how keeping your home clean and choosing the right season can help with keeping your asth-ma under control.
However, the best way to control your asth-ma is to do spirometry daily. Apps like Aluna allow you to track your lung function over time and can even help predict an exacerbation before it occurs. This can reduce your need for control medications and aid in managing your asth-ma.
If you suffer from asth-ma, you CAN control your asth-ma. It doesn’t have to control you.
Watch for These 6 Asthma Warning Signs
Asthma is a common health issue that can be experienced by children and adults. To help prevent a potentially deadly attack, be aware of the potential warning signs for an asth-ma attack. These include shortness of breath, chest tightness, wheezing, difficulty talking, and difficulty swallowing.
Symptoms can come on quickly during normal daily activities. Children with asth-ma should learn to recognize the warning signs so they can get help quickly. Make sure their teachers know about their asth-ma and what to do during a medical emergency.
1. Tight Neck or Chest
As your child’s airways constrict, they might notice a sudden tightening in their neck and chest muscles. This acts as an early indicator of an asth-ma attack. As the muscles tighten and oxygen intake slows, your child may find it challenging to get anything more than a shallow breath.
2. Severe Wheezing or Coughing
An asth-ma attack typically involves coughing attacks that take over the whole body. In individuals who have exercise-induced asth-ma, wheezing or fast breaths are standard after physical activity. While oxygen can enter the body even when coughing or wheezing, the attack may worsen over a short period and become life-threatening.
3. Blue Lips
Blue lips or fingernails indicate there is a lack of oxygen in the blood. Fatigue or brain fog may follow, but ultimately, blue lips show an oncoming asth-ma attack. People with asth-ma may experience an asth-ma attack in 3 seconds or less, so when the signs are present, you must seek immediate relief or call 911.
4. Sudden Anxiety
Another common (but rarely considered) asth-ma attack warning sign is anxiety. Sudden panic is not typically a symptom of asth-ma (unless the individual has lost all ability to breathe). Instead, asth-ma is often physically triggered by anxiety or panic. In other words, if your child suddenly finds themself feeling anxious, they should consider that an asth-ma attack may soon occur as a result.
5. Pale Face and Sweating
The body often breaks out into a cold sweat when an asth-ma attack is about to occur. This can stem from difficult breathing, anxiety, or strain on the body to take in oxygen. Likewise, a pale face and sweating often go hand in hand.
6. Difficulty Speaking
When the airways constrict and prevent oxygen from entering the body, it often messes with other essential functions. The brain becomes clouded, which makes it challenging to formulate thoughts and speak. Shortness of breath also causes difficulty speaking.
The Importance of Monitoring Lung Health
One of the best ways to guard against asth-ma attacks is monitoring your or your child’s lung health. Carefully keeping track of triggers, symptoms, warning signs, and attacks provides essential data for both you and your health care provider. Additionally, an at-home spirometry test to monitor your child’s daily lung function indicates increased and decreased lung capacity.
Empower your child to maintain their asth-ma by teaching them about their lung health and how to use their asth-ma action plan. Knowledge is the best tool people with asth-ma have for controlling their asth-ma.
What Is Silent Asthma?
Silent asthma does not have a clear definition. It isn’t a diagnostic term and is probably used off-the-cuff by some healthcare professionals to refer to silent symptom asth-ma.
Silent symptom asth-ma refers to asth-ma symptoms that don’t make audible noise. Things like coughing or wheezing would not fall into this category. The most common silent symptoms of asth-ma are shortness of breath and tightness in your chest. Although, these two symptoms on their own are rarely enough to diagnose asth-ma.
Other “silent symptoms” of asth-ma may include:
- Fatigue
- Shallow breathing
- Frequent yawning
- Insomnia
- Respiratory infections such as colds
However, these are not technical symptoms of asth-ma, but rather possible side-effects of asth-ma when it isn’t properly treated.
What Is Silent Chest Asthma?
Another term used in conjunction with silent asth-ma is silent chest asth-ma. This term refers to a specific type of asth-ma attack called status asthmaticus. The symptoms of this attack vary but may include:
- Inflammation of the airway
- Little to no wheezing (silence)
- Difficulty breathing
- Hard to detect
Since the symptoms of silent chest asth-ma are hard to detect, they can be challenging to diagnose. However, left untreated, it can be life-threatening. If you believe you may be experiencing symptoms of silent chest asthma, consult your healthcare professional.







Add comment